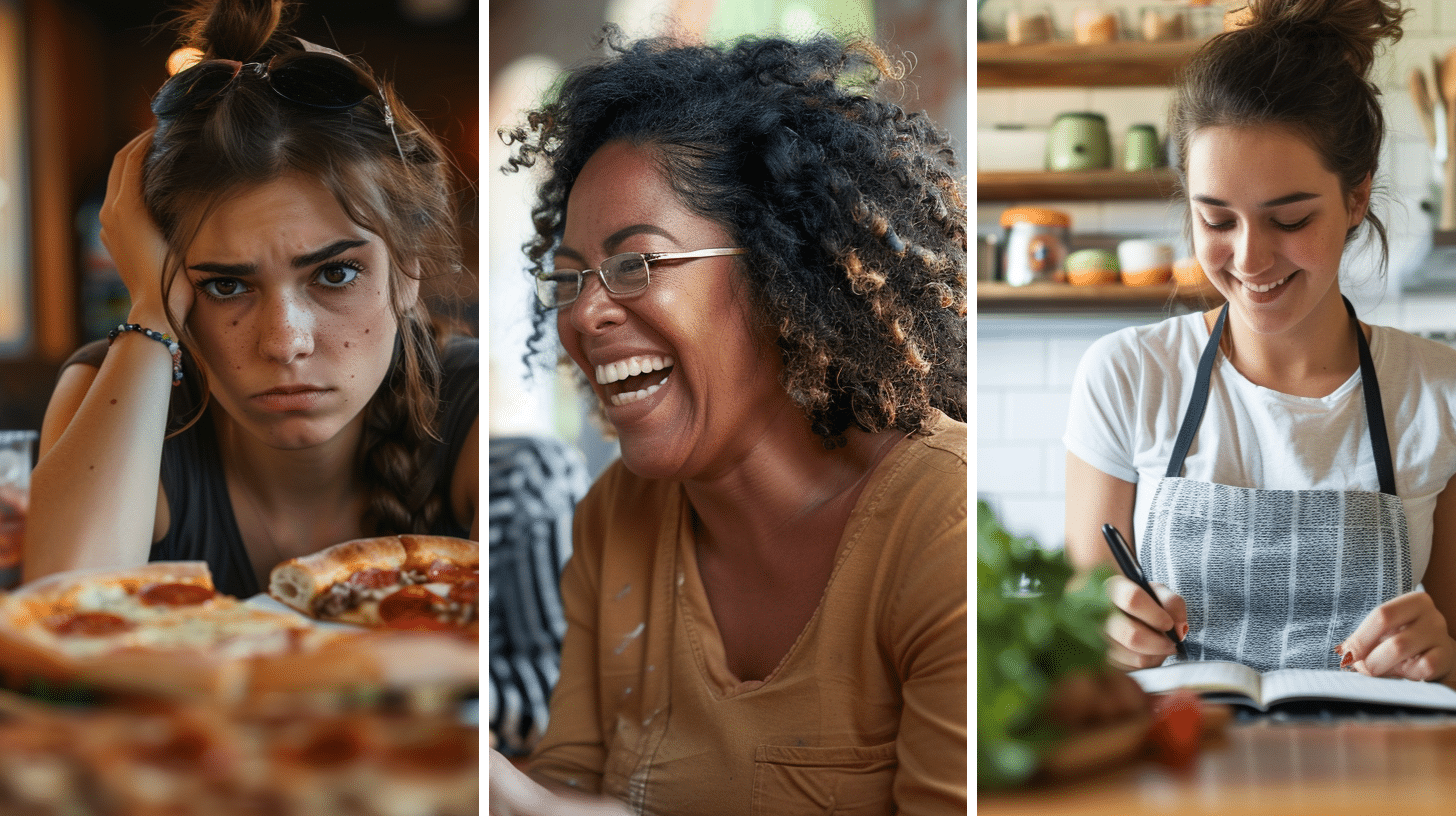
Emotional Eating
Strategies for Breaking the Cycle and Promoting Well-being
Emotional eating is a behavior in which individuals turn to food as a coping strategy to deal with their emotions rather than addressing them directly. It is characterized by consuming large amounts of food, usually high in fat and sugar, to soothe or distract oneself from negative feelings. People often eat emotionally to find comfort, relieve stress, or seek pleasure. However, this coping mechanism can have severe consequences for both mental and physical health, as it often leads to weight gain and related health issues.
Emotional eating can create a vicious cycle, as the guilt and shame associated with overeating can trigger further emotional distress, resulting in more emotional eating. Despite its adverse effects, understanding the reasons behind emotional eating can help individuals develop healthier coping strategies and improve their overall well-being.
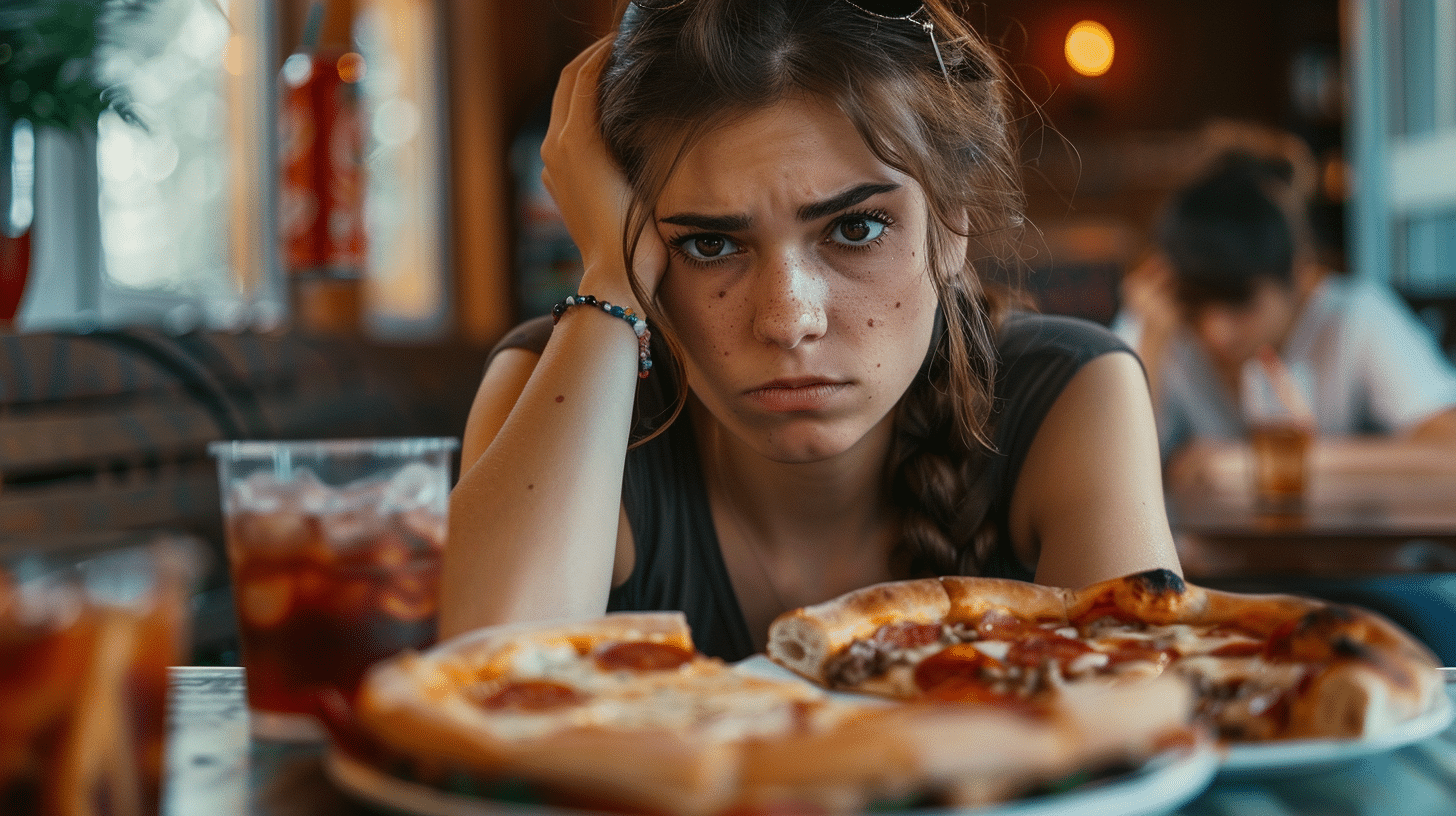

Causes
Emotional eating, a behavior often used as a coping mechanism, stems from various causes that impact individuals’ emotional well-being. Socio-economic disparities play a significant role, with limited access to resources and opportunities due to financial inequality increasing stress and anxiety, leading to reliance on food for comfort. Additionally, the lack of access to education and healthcare leaves individuals without the necessary skills and support to address their emotional and mental health effectively, further contributing to emotional eating behaviors.
Environmental degradation also plays a part, as pollution and loss of natural spaces can generate stress and feelings of unease, prompting individuals to turn to food as a means of solace. Furthermore, systemic discrimination based on factors such as race, ethnicity, gender, or sexuality can lead to increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depression among marginalized individuals, making them more susceptible to emotional eating as a coping mechanism.
Addressing these causes requires reducing socio-economic disparities, ensuring access to education and healthcare, protecting the environment, and dismantling systemic discrimination. By promoting healthier coping mechanisms and emotional well-being, individuals can better manage their emotions and reduce reliance on emotional eating.
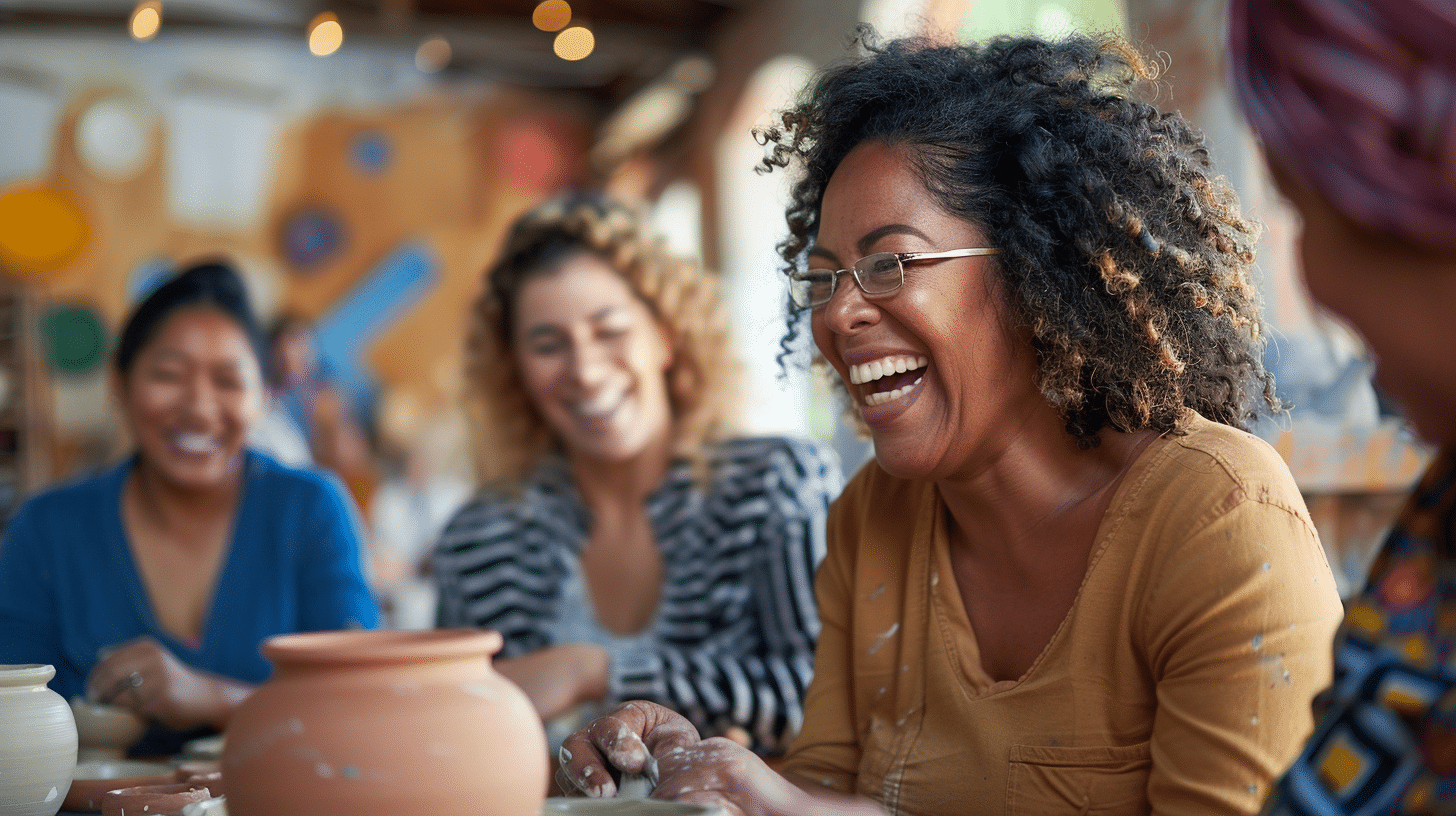

Strategies For Managing Emotional Triggers
Breaking the cycle of emotional eating can be challenging, but with strategies for managing emotional triggers, individuals can take control of their eating habits and overall well-being. One effective approach is identifying personal triggers – those situations, people, or emotions that tend to spark the urge to eat emotionally. This awareness helps individuals recognize the patterns and emotions behind their unhealthy eating habits, often uncovered through keeping a food and mood log, which tracks both emotions and food consumption, facilitating the identification of triggers.
Managing emotional triggers involves finding alternative ways to cope with emotions and satisfy the emotional void that leads to emotional eating. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, like walking, mindfulness, or hobbies, can fill this void without food. Additionally, the “Take Five” method offers a practical technique for interrupting the urge to eat emotionally. When the urge arises, taking a five-minute break to practice deep breathing or mindfulness redirects attention away from food and towards emotions, allowing individuals to make intentional choices about addressing their emotional needs without relying on emotional eating.
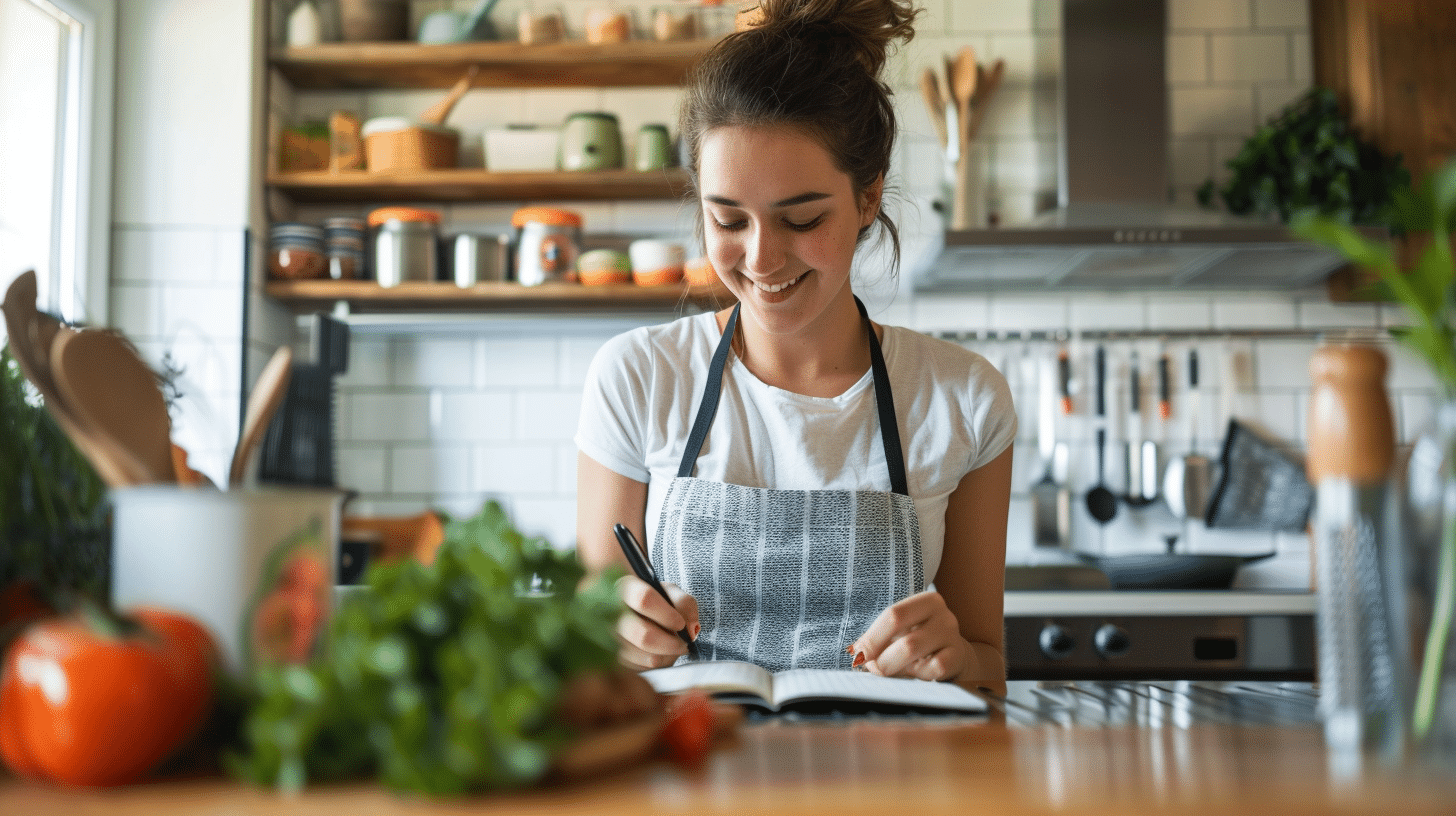

Mindful Eating Techniques
Emotional eating, a common response to stress or other emotional triggers, involves using food for comfort or distraction. Mindful eating offers a powerful solution to this behavior, promoting a healthier relationship with food by cultivating awareness and appreciation for eating without judgment. This practice helps individuals reconnect with their body’s signals, differentiate between physical and emotional hunger, and make more conscious food choices.
Mindful eating techniques help individuals distinguish physical hunger, characterized by specific sensations like a growling stomach, from emotional hunger, often driven by non-physical cues such as stress or boredom. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can tune into their bodily sensations to identify whether their hunger is a need for sustenance or an emotional craving. Recognizing emotional hunger allows for implementing strategies to manage emotions, like engaging in self-care or seeking support.
Various strategies can be used to incorporate mindful eating into daily life. These include eating slowly and savoring each bite, paying attention to taste, texture, and smell, listening to hunger and fullness cues, starting to eat when hungry, and stopping when satisfied. Engaging all senses while eating, such as noticing colors and sounds, enhances the mindfulness experience. By adopting these strategies, individuals can transform their relationship with food, breaking the cycle of emotional eating and promoting a more balanced approach to nourishment.
Taking Control of Emotional Eating
Understanding the complexities of emotional eating and its underlying causes is crucial for developing healthier coping mechanisms. By identifying personal triggers, practicing mindfulness, and adopting mindful eating techniques, individuals can break free from the cycle of emotional eating and improve their overall well-being. If you’re struggling with emotional eating and seeking support for weight loss, contact Medical Health Solutions to schedule a weight loss consultation at (303) 951-8617.
We provide weight loss services for these Lone Tree, Colorado areas:
Lone Tree, Acres Green, Belvedere, Bluffmont Estates, Carriage Club, Centennial Ridge, Club Terrace, Country Club Estates, Cypress Green, Douglas County, Fairways At Lone Tree, Heritage Estates, Heritage Hills, Lincoln Square Lofts, Masters Park, Montecito, Prominence Point, Ridgegate, Taos of Lone Tree, Terra Ridge, The Fairways, and Wildcat Ridge.
We also provide weight loss services for Edgewater, Colorado and these surrounding areas:
Edgewater, Wheat Ridge, Arvada, Westminster, Granite, Golden, Englewood, Littleton, Broomfield, Dupont, Commerce City, Morrison, and Henderson.
We also provide weight loss services for these Denver, Colorado areas:
Denver, Baker, Capitol Hill, Central Business District, Cheesman Park, Cherry Creek, City Park, City Park West, Civic Center, Congress Park, Country Club, Lincoln Park, North Capitol Hill, Speer, Union Station, Belcaro, Cory-Merrill, East Colfax, Hale, Hilltop, Indian Creek, Lowry, Montclair, Park Hill, Virginia Village, Washington Virginia Vale, Windsor, Clayton, Cole, Elyria-Swansea, Five Points, Globeville, North Park Hill, Skyland, South Park Hill, Whittier, Central Park, Gateway, Green Valley Ranch, Montbello, Northeast Park Hill, Auraria, Berkeley, Chaffee Park, Highland, Jefferson Park, Regis, Sloan Lake, Sunnyside, West Highland, College View, South Platte, Overland, Platt Park, Rosedale, University, University Hills, University Park, Washington Park, Washington Park West, Wellshire, Goldsmith, Hampden, Hampden South, Kennedy, Southmoor Park, Southwest, Bear Valley, Fort Logan, Harvey Park, Harvey Park South, Marston, West, Public housing in Sun Valley., Athmar Park, Barnum, Barnum West, Mar Lee, Ruby Hill, Sun Valley, Valverde, Villa Park, West Colfax, and Westwood.